Meet Lilly,
Lilly is a sweet older girl.
We met her for the first time for evaluation of a swollen belly. On palpation of her abdomen by Dr. Ortner, it was noted that she had a large mass. X-rays and subsequently an abdominal ultrasound with a biopsy showed that her mass in her abdomen was a benign fatty mass, an intra-abdominal lipoma. The mass did not appear to affect any of her internal organs and she was deemed a good surgical candidate. On recheck pre-surgical examination it was also noted that Lilly had a tumor of her anal gland. A needle biopsy was performed showing that the mass was cancerous, an anal sac adenocarcinoma. So now Lilly has 2 masses, a benign one in her abdomen and an aggressive cancer in her anal sac.
Lilly went to surgery to have both masses removed under the same anesthesia. I was able to remove the fatty mass from the abdomen without complication, as it did not involve any vital internal organs. The fatty mass in the belly weighed 8 ½ pounds. Lilly was then prepped and had her anal sac tumor removed as well. All in total Lilly was under anesthesia for about 2 ½ hours and did wonderful.
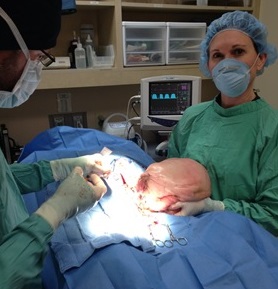
Lipomas are benign fatty tumors that usually arise from the body’s subcutaneous tissues. They are most commonly found on the trunk, in the groin and along the limbs. Rarely do they grow from the fat deposits in the abdomen. When they do, they are still benign in nature. However they cause problems by compressing the internal organs. In Lilly’s case, her lipoma was nearly 15% of her body weight. She was truly a new dog after surgery.
Anal sac adenocarcinomas are an aggressive cancer of the anal sacs. They tend to spread (metastasize) to the local lymph nodes and to the lungs. As well they can cause the body’s calcium levels to increase. If caught early prior to spread of the cancer, the prognosis with surgery is favorable.
A rectal exam should be part of every physical exam in older patients. The majority of the masses we find in practice are incidental. Meaning we find them before they cause problems. If left untreated or later in the stage of the disease, common clinical signs include:
– Swelling adjacent to the rectum
– Constipation
– Straining to defecate or pain on defecation
– Bloody stool
– Increased thirst and urination secondary to elevated blood calcium levels
By: Dr. Jon Perchick


